— A beginner-friendly guide with real-world and African examples
By now, we’ve established that data annotation is the backbone of artificial intelligence. It’s how we teach machines to see, read, hear, and understand the world around us. But did you know there are different types of annotation, each designed to train specific types of AI models?
In this post, we’ll explore:
- The major types of data annotation
- The kind of data each is used for
- Real-world examples (including African use cases)
- The skills and tools needed to perform them
Whether you’re curious about AI or considering a career in Data Annotation, this guide will help you understand where human input makes the most impact.
1. Image Annotation
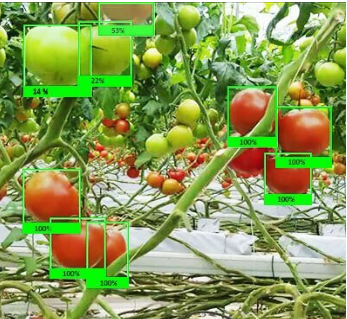
Image annotation involves labelling parts of an image to help machines recognise objects, faces, patterns, or scenes.
How it Works:
Annotators mark and label specific regions in an image using shapes like boxes, lines, or polygons.
Common Types:
- Bounding boxes: Outline standard-shaped objects like vehicles or bottles
- Polygon annotation: Used for irregular shapes like trees, road edges
- Key-point annotation: Highlights object parts like eyes, joints, or limbs
Real-World Examples:
- E-commerce sites (like Jumia) tag product images
- Self-driving cars detect pedestrians and road signs
- Agritech tools identifying diseased vs healthy plants
Tools & Skills:
- Tools: CVAT, Label Studio, V7
- Skills: Precision, attention to detail, basic computer vision knowledge
2. Text Annotation
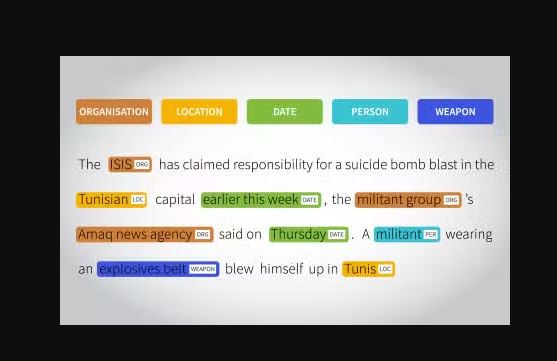
Text annotation is the process of labelling textual data so that machines can understand and generate human language, essential for Natural Language Processing (NLP).
How It Works:
Annotators highlight words, phrases, or sections based on meaning, sentiment, or intent.
Common Types:
- Named Entity Recognition (NER): Tagging names of people, brands, places
- Sentiment Analysis: Classifying tone as positive, negative, or neutral
- Intent Classification: Understanding user goals like “book a flight” or “cancel order”
Real-World Examples:
- Chatbots understand customer service questions
- Social media tools analysing public sentiment
- Translation apps convert Yoruba or Hausa into English.
]
Tools & Skills:
- Tools: Prodigy, Doccano, LightTag
- Skills: Strong grammar, language awareness, cultural context
3. Audio Annotation
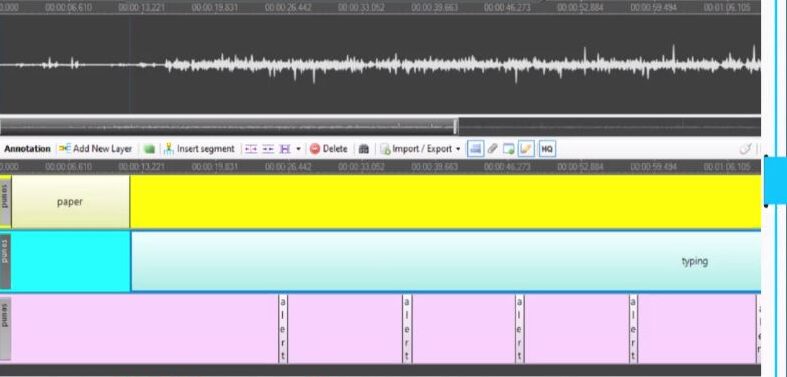
Audio annotation is the labelling of sounds or speech so AI can interpret tone, language, or environmental noise.
How it Works:
Annotators listen to audio clips and label speech, emotions, background sounds, or speaker identities.
Common Types:
- Speech transcription: Turning speech into text
- Speaker labelling: Identifying who is speaking
- Emotion annotation: Tagging tones like happy, angry, or calm
- Sound tagging: Identifying sounds like footsteps or sirens
Real-World Examples:
- Voice assistants like Siri or Alexa
- Call centres analysing customer tone
- Language learning apps training on African dialects
Tools & Skills:
- Tools: Audacity, Praat, Label Studio Audio
- Skills: Good hearing, patience, and language proficiency
4. Video Annotation
![]()
Video annotation involves labelling objects and activities across a sequence of frames, helping AI understand motion and time-based context.
How it Works:
Annotators tag objects or people in multiple video frames, often tracking their movement over time.
Common Types:
- Object tracking: Following a person or object through a scene
- Activity recognition: Identifying actions like running or waving
- Scene classification: Labelling entire scenes such as “crowd” or “office”
Real-World Examples:
- Security systems detect suspicious movement
- Sports analytics track athlete performance
- Livestock monitoring in precision agriculture
Tools & Skills:
- Tools: V7, CVAT, VIA
- Skills: Frame consistency, attention to movement, video playback skills
5. 3D Point Cloud Annotation
3D point cloud annotation is used to label objects in 3D space, helping AI understand depth and spatial relationships, especially in robotics and autonomous vehicles.
How It Works:
Annotators work with data collected from LIDAR or depth sensors, tagging objects in a “cloud” of 3D points.
Real-World Examples:
- Self-driving cars detect object distance
- Drones mapping rural communities
- Delivery robots navigate complex spaces.
Tools & Skills:
- Tools: Supervisely, Scale AI
- Skills: Spatial reasoning, technical familiarity with 3D environments
So, Which Type Is Right for You?
Each type of Data Annotation supports one or more types of machine learning models, and each opens a unique door in AI development.
| Annotation Type | Best For | Beginner-Friendly? |
| Image | Computer vision, agriculture, and retail | ✅ Yes |
| Text | Chatbots, NLP, translation | ✅ Yes |
| Audio | Voice assistants, call centres | ⚠️ Intermediate |
| Video | Surveillance, sports, agri-tech | ⚠️ Intermediate |
| 3D Point Cloud | Robotics, drones, self-driving cars | 🔧 Advanced |
In Summary
Data annotation isn’t one-size-fits-all. Each machine learning model depends on carefully labelled data, and every annotation type requires its own tools, skills, and context. By understanding the different types of Data Annotation, you can:
- Discover what’s right for your career path
- Learn what industries rely on these skills
- Prepare to work on real AI training datasets
Want to Become a Data Annotator?
Beyond Human Intelligence (BHI) offers hands-on training in image, text, audio, and video annotation created for beginners looking to break into the AI and data industry.
📩 Our next training cohort is coming soon!
Want to be the first to know when registration opens?
👉 Join the waitlist today, and we’ll send you early access, program details, and exclusive free resources to help you prepare.






